Grid Search¶
does this and that…
-
class
olympus.planners.Grid(goal='minimize', levels=2, budget=None, exceed_budget=True, shuffle=False, random_seed=None)[source] Grid search.
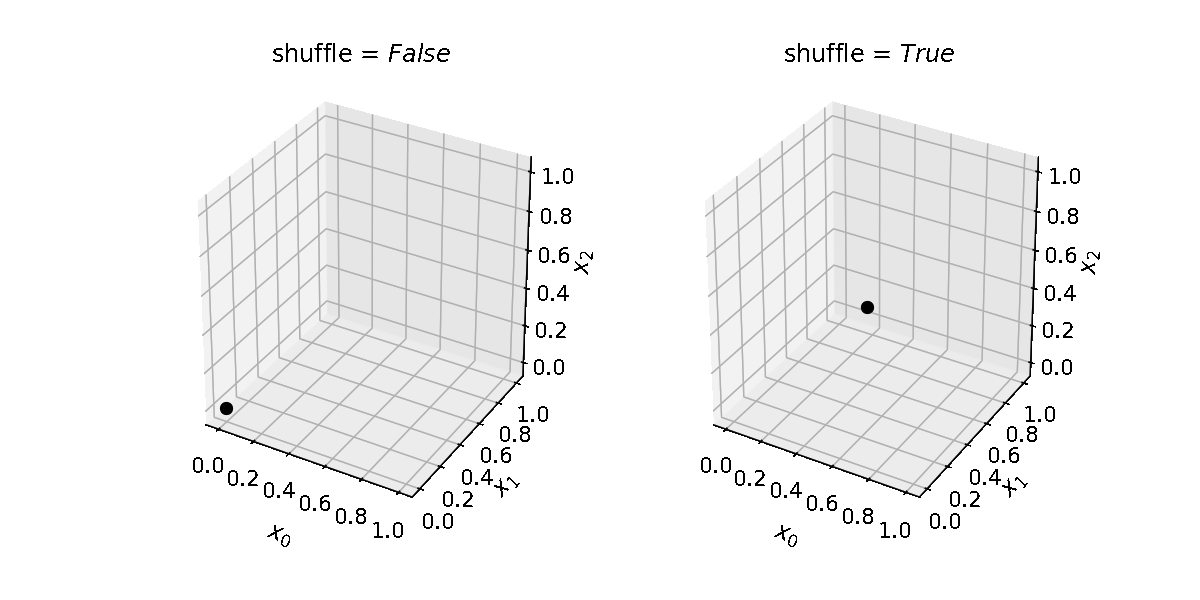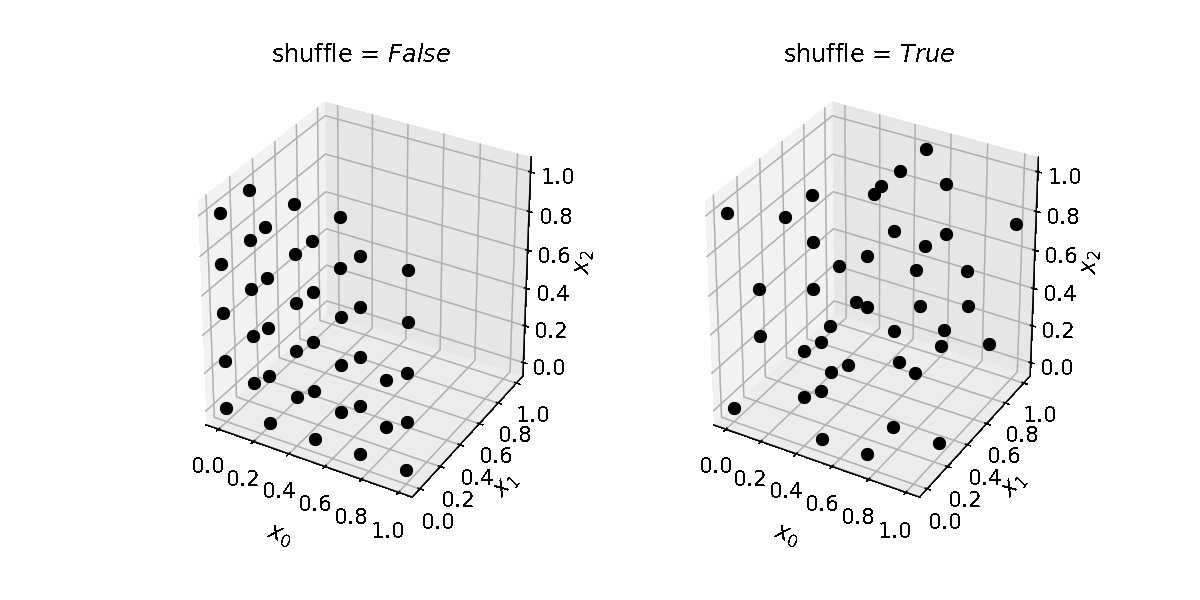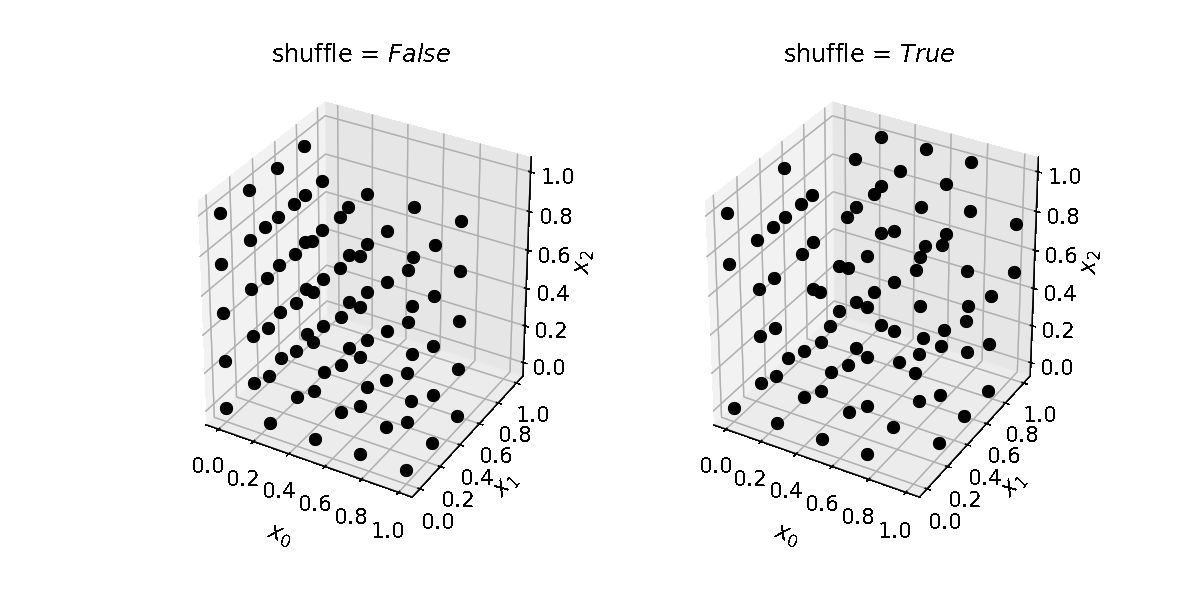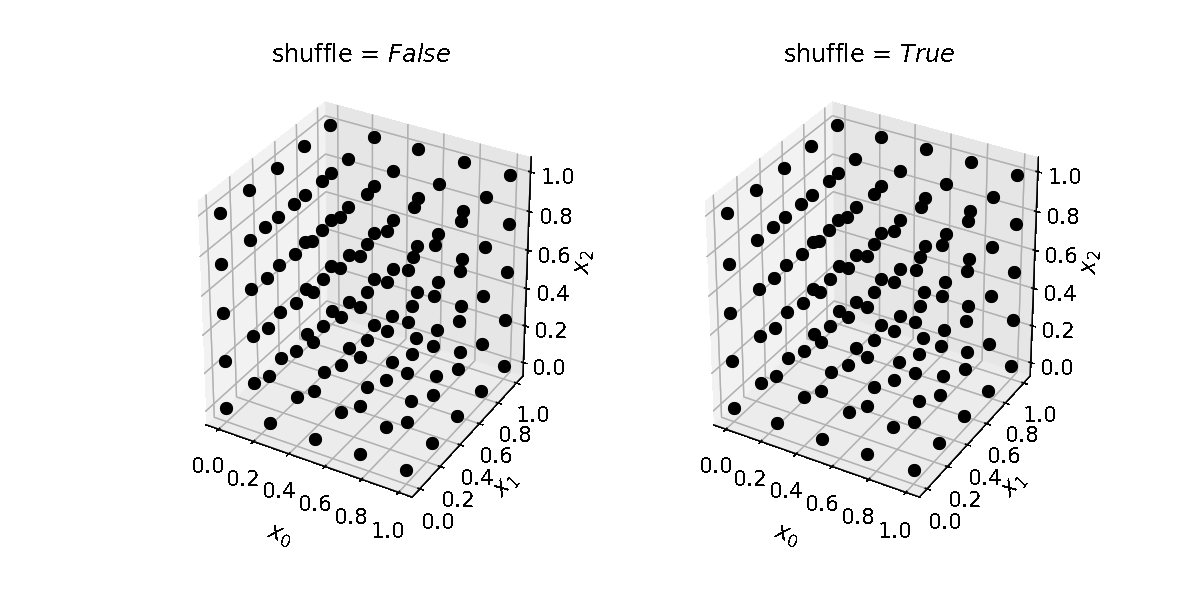
Note that the number of samples grow exponentially with the number of dimensions. E.g. for a 2-dimensional parameter space, with 2 levels, the grid will contain 4 samples; for a 3-dimensional space, it will contain 8 samples; for a 6-dimensional space, 64 samples.
- Parameters
goal (str) – The optimization goal, either ‘minimize’ or ‘maximize’. Default is ‘minimize’.
levels (int, list) – How many locations in parameter space to sample per parameter/dimension. If an integer is provided, the same number of levels will be used for each dimension. Provide a list to use different levels for different dimensions. Default is 2.
budget (int) – Maximum number of samples you want to evaluate. From the specified
budgetan adequate value for the levels will be derived. Note that, if provided, the argumentlevelswill be discarded. Default is None.exceed_budget (bool) – Whether to allow building the grid with more samples then
budget. This means some points might not be evaluated, but ensures there will be enough grid points to run as many evaluations as defined inbudget. If False, the number of grid points will be less or equal tobudget; this guarantees the budget is enough to guarantee the exploration of the whole grid. Default is True.shuffle (bool) – Whether to randomize the order of the samples in the grid. Default is False.
random_seed (int) – Random seed. Set a random seed for a reproducible randomization of the grid if
shufflewas set to True.
Methods
tell([observations])Provide the planner with all previous observations.
ask([return_as])suggest new set of parameters
recommend([observations, return_as])Consecutively executes tell and ask: tell the planner about all previous observations, and ask about the next query point.
optimize(emulator[, num_iter, verbose])Optimizes a surface for a fixed number of iterations.
reset()Clears the remaining samples in the grid and prepares the planner for re-initialisation.
-
ask(return_as=None) suggest new set of parameters
- Parameters
return_as (string) – choose data type for returned parameters allowed options (dict, array)
- Returns
newly generated parameters
- Return type
ParameterVector
-
optimize(emulator, num_iter=1, verbose=False) Optimizes a surface for a fixed number of iterations.
- Parameters
emulator (object) – Emulator or a Surface instance to optimize over.
num_iter (int) – Maximum number of iterations allowed.
verbose (bool) – Whether to print information to screen.
- Returns
- Campaign object with information about the optimization, including all parameters
tested and measurements obtained.
- Return type
campaign (Campaign)
-
recommend(observations=None, return_as=None) Consecutively executes tell and ask: tell the planner about all previous observations, and ask about the next query point.
- Parameters
observations (list of ???) –
return_as (string) – choose data type for returned parameters allowed options (dict, array)
- Returns
newly generated parameters
- Return type
list
-
reset()[source] Clears the remaining samples in the grid and prepares the planner for re-initialisation.
-
set_param_space(param_space) Defines the parameter space over which the planner will search.
- Parameters
param_space (ParameterSpace) – a ParameterSpace object defining the space over which to search.
-
tell(observations=<olympus.campaigns.observations.Observations object>) Provide the planner with all previous observations.
- Parameters
observations (Observations) – an Observation object containing all previous observations. This defines the history of the campaign seen by the planner. The default is None, i.e. there are no previous observations.